1.
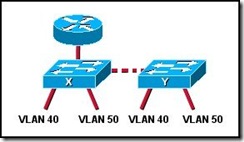
Refer to the exhibit. What will allow a host on VLAN 40 on switch X to communicate with a host in VLAN 40 on switch Y?
QoS
routing
trunking
VPN
2.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator needs to setup Switch1 for remote access from HostA. The show ip interface brief is issued on Router1 and the show interfaces trunk command is issued on the Switch1 to verify the current status. The administrator applies the additional configuration shown in the exhibit to Switch1. However, the telnet from HostA fails. What additional commands need to be applied to the switch?
Switch(config)# interface vlan 1
Switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.250 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Switch(config-if)# ip default-gateway 10.1.10.254
Switch(config)# interface vlan 1
Switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.50.250 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Switch(config-if)# ip default-gateway 10.1.50.254
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.10.250 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Switch(config-if)# ip default-gateway 10.1.10.254
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.250 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Switch(config-if)# ip default-gateway 10.1.10.254
Switch(config)# interface vlan 50
Switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.10.250 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Switch(config-if)# ip default-gateway 10.1.10.254
3

Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true regarding what the cost value of 23 represents for Switch4? (Choose two.)
This cost represents the lowest cost path for Switch4 to the root switch.
A cost of 23 is the value being advertised out port 16 on the switch upstream (closer) to the root switch.
Switch4 adds the cost of a Fast Ethernet link to 23 to determine its total cost to reach the root switch.
Switch4 is connected via a Fast Ethernet link to an upstream switch that in turn is directly connected to the root switch via a Gigabit Ethernet link.
The root switch is advertising a cost of 23, which is lower than any other switch in the VLAN0001 spanning-tree domain.
4

Refer to the exhibit. The switches in the exhibit have VTP pruning enabled. Which VLANs will be pruned from switch SW3?
VLAN 10 and VLAN 20
VLAN 1, VLAN 10, and VLAN 20
VLAN 1, VLAN 1002 through 1005
VLAN 1, VLAN 10, VLAN 20, VLAN 1002 through 1005
5. Which method establishes an administrative connection for configuring the Linksys WRT300N wireless access point?
Associate with the access point and then open a HyperTerminal session with the access point.
Physically connect to the access point and then reboot the computer to launch the configuration software.
From a computer in the same IP subnet as the access point, enter the default IP address of the access point in a web browser.
Modify the TCP/IP properties of the computer connected to the access point so that it exists on the same network, and then reboot your computer to establish a connection.
6. Refer to the exhibit. Router RA receives a packet with a source address of 192.168.1.35 and a destination address of 192.168.1.85. What will the router do with this packet?
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.1.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.3.
The router will forward the packet out interface FastEthernet 0/1.2 and interface FastEthernet 0/1.3.
The router will ignore the packet because the source and destination are on the same broadcast domain.
The router will drop the packet since no network that includes the source address is attached to the router.
7. What are three benefits of a hierarchical network model? (Choose three.)
reduced contention for bandwidth
reduced size of the physical layout
increased fault tolerance of the network
elimination of the need for wiring closets
elimination of the need for layer three functionality
simplification of management and troubleshooting
8. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true regarding the information shown?
Only one VLAN is currently configured to use the trunk links.
The switch negotiated trunk links for interfaces Fa0/1 and Gi0/1.
A Cisco proprietary protocol is in use for interfaces Fa0/1 and Gi0/1.
Interfaces Gi0/1 and Fa0/1 are allowed to carry data from multiple VLANs.
9

Refer to the exhibit. What does STATIC indicate in the output that is shown?
The switch will not allow any other device to connect to port Fa0/15.
Traffic destined for MAC address 0000.c123.5432 will be forwarded to Fa0/15.
This entry will be removed and refreshed every 300 seconds to keep it in the table.
The switch learned this MAC address from the source address in a frame received on Fa0/15.
When processing a frame, the switch does not have to perform a lookup to determine the final destination port.
10
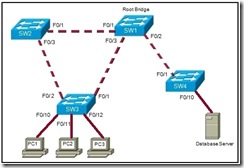
Refer to the exhibit. What is the consequence if SW1 port F0/1 is configured as an edge port?
SW1 port F0/1 transitions to the learning state.
SW1 port F0/1 can generate a temporary loop.
SW1 port F0/1 becomes a non-designated port.
SW1 port F0/2 no longer passes BPDUs to SW4.
11
Which three statements are true regarding router-on-a-stick inter-VLAN routing? (Choose three.)
requires the use of subinterfaces on the router
requires an access link between the router and Layer 2 switch
more cost-efficient and scalable than using multiple physical interfaces
requires each subinterface to be configured with the no shutdown command
can impact performance if many VLANs compete for bandwidth on a single router interface
makes troubleshooting the inter-VLAN routing configuration much less complex than when using multiple physical interfaces
12
Which two statements describe Spanning Tree Protocol? (Choose two.)
It eliminates Layer 2 loops in network topologies.
It eliminates the need for redundant physical paths in network topologies.
It can only be used in networks in which Layer 2 switching is in use.
It can only be used in networks where both routers and switches are used together.
It can only be used in networks where routers are installed.
13
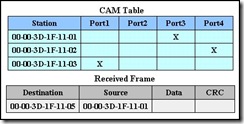
Refer to the exhibit. An Ethernet switch has developed the CAM table shown. What action will the switch take when it receives the frame shown at the bottom of the exhibit?
forward the frame out all interfaces except Interface3
add station 00-00-3D-1F-11-05 to Interface2 in the forwarding table
forward the frame out Interface3
discard the frame
forward the frame out all interfaces
forward the frame out Interface2
14
Which parameter is used to uniquely identify one wireless network from another?
SSID
OFDM
WEP
DSSS
15

Refer to the exhibit. A new host needs to be connected to VLAN 1. Which IP addresses should be assigned to this new host?
192.168.1.11 /28
192.168.1.22 /28
192.168.1.33 /28
192.168.1.44 /28
192.168.1.55 /28
16
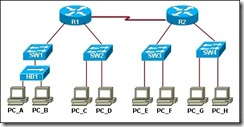
Refer to the exhibit. Hosts PC_A and PC_B send traffic simultaneously, and the frames from the transmitting stations collide. What is the last device to receive the collision?
hub HB1
switch SW1
router R1
switch SW2
router R2
switch SW4
17
What VLANs are allowed across a trunk when the range of allowed VLANs is set to the default value?
All VLANs will be allowed across the trunk.
Only VLAN 1 will be allowed across the trunk.
Only the native VLAN will be allowed across the trunk.
The switches will negotiate via VTP which VLANs to allow across the trunk.
18
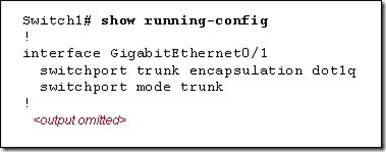
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the configuration shown, how will an Ethernet frame on port GigabitEthernet0/1 be modified?
802.1Q encapsulation prepends a 4-byte tag field in front of the original Ethernet frame and recomputes the frame check sequence (FCS) on the modified frame.
802.1Q encapsulation inserts a 4-byte tag field into the original Ethernet frame between the source address and type/length fields and recomputes the frame check sequence (FCS) on the modified frame.
802.1Q encapsulation prepends an 802.1p field in front of the original Ethernet frame and recomputes the frame check sequence (FCS) on the modified frame.
802.1Q encapsulation inserts an 802.1p field into the original Ethernet frame between the source address and type/length fields and recomputes the frame check sequence (FCS) on the modified frame.
19

Refer to the exhibit. Computer A sends a broadcast message. Which devices will see the broadcast?
computer B
computer B and Router1
computer C and Router1
computer B, computer D, computer E and Router1
computer B, computer C, computer D, computer E and Router1
computer A, computer B, computer C, computer D, computer E and Router1
20

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to implement inter-VLAN routing on a hierarchical network. On which devices should the inter-VLAN routing be configured?
AS1 and AS2
DS1 and DS2
Gateway and CS1
Gateway, CS1, DS1, and DS2
21

Refer to the exhibit. Spanning-tree port priorities are 128 for all interfaces. The network administrator enters the spanning-tree vlan 1 root primary command on S4. Which two port results are correct? (Choose two.)
S1 Gi0/1 becomes a root port.
S2 Gi0/2 becomes a non-designated port.
S3 Gi0/1 becomes a non-designated port.
S4 Gi0/1 becomes a root port.
S4 Gi0/2 becomes a designated port.
22
What is the purpose of issuing the command switchport mode access on a switch interface?
disable port security
make the port operational
override the default port behavior
force the port to be a part of a single vlan
23
Which identifier is used to keep track of frames that are destined for a particular wireless client?
AID
SSID
BSSID
ESSID
24
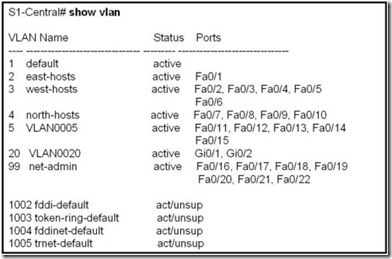
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator needs to remove the east-hosts VLAN and use the switch port from that VLAN in one of the existing VLANs. What two commands should be used when completely removing VLAN 2 from S1-Central while leaving the switch and all its interfaces operational? (Choose two.)
S1-Central# reload
S1-Central# erase flash:
S1-Central(config)# no vlan 2
S1-Central# delete flash:vlan.dat
S1-Central(config-if)# switchport access vlan 3
25
What two methods can be used to remove MAC address table entries from a switch? (Choose two.)
Power cycle the switch to clear all dynamically learned addresses.
The clear switching-tables command will remove statically configured entries.
The clear mac-address-table command will remove statically and dynamically configured table entries.
The erase flash command will clear all statically configured table entries.
Statically configured MAC addresses will automatically be removed from the address table 300 minutes after the last activity on a switch port.
26

Refer to the exhibit. What will happen when frames that contain an unknown source address reach interface fa0/24?
A syslog message will be logged.
Fa0/24 will become error-disabled.
The incoming frames will be dropped.
The security violation count will be incremented.
27

Refer to the exhibit. What does "FORWARDING" mean in the command output shown?
The switch is sending and receiving data frames.
The switch is receiving BPDUs, but not sending data frames.
The switch is participating in an election process by forwarding the BPDUs it receives.
The switch is receiving BPDUs and populating the MAC address table, but not sending data.
28

Refer to the exhibit. Hosts A and B, connected to hub HB1, attempt to transmit a frame at the same time but a collision occurs. Which hosts will receive the collision jamming signal?
only hosts A and B
only hosts A, B, and C
only hosts A, B, C, and D
only hosts A, B, C, and E
29

Refer to the exhibit. The switches are configured for VTP as shown. Which two statements correctly describe the operation of these switches? (Choose two.)
A new VLAN can be added to Switch1 and that information will be added only to Switch2.
A new VLAN can be added to Switch1 and that information will be added to Switch2 and Switch4.
An existing VLAN can be deleted from Switch4 and that VLAN will be deleted from Switch1 and Switch2.
An existing VLAN can be deleted from Switch2 and that VLAN will be deleted from Switch1 and Switch4.
A new VLAN can be added to Switch4 and that information will be added to Switch1, Switch2, and Switch3.
A new VLAN can be added to Switch3 and that information will be added to Switch1, Switch2, and Switch4.
30

Refer to the exhibit. Both switches are interconnected via a trunk link. Host A and host B are on the default VLAN but are not able to exchange traffic. What should be done to fix the problem?
Allow all VLANs on the trunk link.
Remove the native VLAN from the trunk.
Include a router or switch with Layer 3 capabilities.
Configure the same native VLAN on both ends of the trunk.
31

Refer to the exhibit. Which two facts can be confirmed by this output? (Choose two.)
This switch shows no configuration revision errors.
This switch has established two-way communication with the neighboring devices.
This switch is configured to advertise its VLAN configuration to other VTP-enabled switches in the same VTP domain.
This switch will drop all VTP advertisements that come from the switches that are configured in the same VTP domain.
This switch will cause no disruption in the VTP domain operations if the rest of the switches in the same VTP domain have a higher configuration revision number.
32. Why is it important that the network administrator consider the spanning-tree network diameter when choosing the root bridge?
The network diameter limitation is 9.
BPDUs may be discarded because of expiring timers.
The cabling distance between the switches is 100 meters.
The network diameter must be set to the number of meters of the cable between the root bridge and its farthest connected switch.
33.
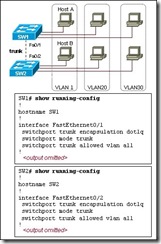
Refer to the exhibit. How does SW1 manage traffic coming from Host A?
SW1 drops the traffic because it is untagged.
SW1 leaves the traffic untagged and forwards it over the trunk.
SW1 tags the traffic with the lowest VLAN ID value and forwards it over the trunk link.
SW1 encapsulates the traffic with 802.1Q encapsulation and forwards it over the trunk link.
34
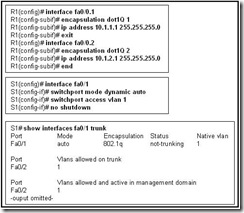
Refer to the exhibit. After the listed commands are entered into router R1 and switch S1, the administrator enters the show interface fa0/1 trunk and gets the results shown. What is the likely problem?
The trunk is established, but no VLANs have been configured to use it.
The trunk has not been established because the router does not support dynamic trunking protocol.
The router, the switch, or both must be configured with the dynamic desirable option for dynamic trunking protocol to establish a trunk.
The router is missing the dynamic trunking protocol statements necessary to form a trunk.
35

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters the configuration shown to allow both SSH and Telnet connections to the switch. The Telnet connections fail. What is the most likely cause of this problem?
The SSH version number is wrong.
SSH has been configured on the wrong line.
Telnet and SSH cannot be configured simultaneously.
The transport input command is configured incorrectly.
36

Refer to the exhibit. Each switch is shown with its MAC address. Which switch will be elected as the spanning-tree root bridge if the switches are configured with their default priority values?
switch A
switch B
switch C
switch D
switch E
switch F
37

Refer to the exhibit. Which switch will be elected as the root bridge of the spanning tree topology?
Cat-A
Cat-B
Cat-C
Cat-D
38. What are two benefits of the IEEE 802.11n standard over the IEEE 802.11G? (Choose two.)
requires less equipment
provides improved range
permits increased data rates
has a single-input and a single-output
needs no hardware upgrade for compatibility
39
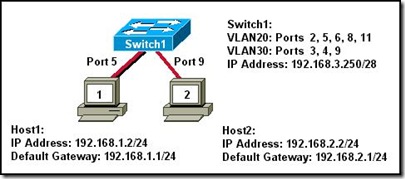
Refer to the exhibit. What three statements describe why Host1 and Host2 are unable to communicate? (Choose three.)
The switch ports are on different VLANs.
The switch IP address is on the wrong subnet.
The hosts are configured on different logical networks.
A router is required to forward traffic between Host1 and Host2.
The VLAN port assignments must be contiguous for each VLAN.
The host default gateway addresses must be on the same logical network.
40

Refer to the exhibit. Which three options correctly identify information that could be associated with this output?(Choose three.)
Interface FastEthernet3/0/0 is subinterfaced.
A non-proprietary trunking protocol is in use.
The configuration is appropriate for a router-on-a-stick network design.
A shutdown command has been applied to interface FastEthernet3/0/0.
Interface FastEthernet3/0/0.3 is mapped to the default management VLAN.
An IP address should be applied to FastEthernet3/0/0 for correct data routing.
41. Which statement regarding the service password-encryption command is true?
The service password-encryption command is entered at the privileged EXEC mode prompt.
The service password-encryption command encrypts only passwords for the console and VTY ports.
The service password-encryption command encrypts all previously unencrypted passwords in the running configuration.
To see the passwords encrypted by the service password-encryption command, enter the no service password-encryption command.
42. Which three statements are correct concerning the default configuration of a new switch? (Choose three.)
Spanning Tree Protocol is disabled.
Enable password is configured as cisco.
All switch ports are assigned to VLAN1.
The flash directory contains the IOS image.
VLAN1 is configured with a management IP address.
All interfaces are set to auto-negotiation of speed and duplex.
43
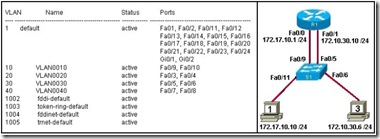
Refer to the exhibit. R1 is configured for traditional inter-VLAN routing. R1 can ping computer 3 but cannot ping computer 1. What is a possible cause for this failure?
S1 port Fa0/11 is in the wrong VLAN.
R1 does not have an active routing protocol.
The IP address of computer 1 is in the wrong logical network.
Router interface Fa0/0 has the wrong trunk encapsulation type configured.
44

Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true about the operation of the interfaces? (Choose two.)
Incoming traffic with VLAN ID 0 is processed by interface fa0/0.
Incoming traffic that has a VLAN ID of 2 is processed by subinterface fa0/0.2.
Both subinterfaces remain up with line protocol up, even if fa0/0 line protocol is down.
Subinterfaces use unique MAC addresses by adding the 802.1Q VLAN ID to the hardware address.
Traffic inbound on this router is processed by different subinterfaces, depending on the VLAN from which the traffic originated.
45
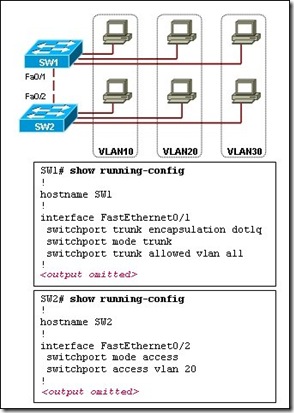
Refer to the exhibit. The hosts connected to switch SW1 are not able to communicate with the hosts in the same VLANs connected to switch SW2. What should be done to fix the problem?
Configure VLANs with different VLAN IDs on switch SW2.
Reconfigure the trunk port on switch SW2 with static trunk configuration.
Introduce a Layer 3 device or a switch with Layer 3 capability in the topology.
Apply IP addresses that are in the same subnet to the interfaces used to connect SW1 and SW2.
46. In which mode is a VTP switch operating if it has been configured to only forward VTP advertisements?
client
root
server
transparent
47

Refer to the exhibit. Switch SW2 was tested in a lab environment and then inserted into a production network without reloading its configuration. After the trunk link between SW1 and SW2 was brought up, all users lost connectivity to the network. What could be the source of the problem?
All the VLANs were pruned from the trunk port between SW1 and SW2.
SW1 and SW2 cannot be both set as VTP servers in the same VTP domain.
VTP configuration revision number of SW2 was higher than the configuration revision number of SW1.
The additional VLANs from SW2 created more VLANs than the VLAN database of SW1 could contain.
48. What three tasks should be performed before moving a Catalyst switch to another VTP management domain? (Choose three.)
Select the correct VTP mode and version.
Configure the switch with the name of the new management domain.
Download the VTP database from the VTP server in the new domain.
Configure the VTP server in the new domain to recognize the BID of the switch.
Reset the VTP counters to allow the switch to synchronize with the other switches in the new domain.
Verify that the switch has a lower configuration revision number than the other switches in the new domain.
49

Refer to the exhibit. Switch SW2 has been newly purchased and added to the network. What configuration should be applied to SW2 so that it participates in the same VTP domain as switch SW1, receives VLAN information from SW1, and synchronizes VLAN information?
Disable VTP pruning on SW2.
Configure SW2 in VTP transparent mode.
Configure SW2 with the VTP domain password.
Configure SW2 as a VTP server with a higher revision number.
50

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has segmented the network into two VLANs and configured Router1 for inter-VLAN routing. A test of the network, however, shows that hosts on each VLAN can only access local resources and not resources on the other VLAN. What is the most likely cause of this problem?
Switch port Fa0/1 is not trunking.
Router interface Fa0/0 is possibly down.
No routing protocol is configured on Router1.
One of the router subinterfaces is possibly down.
51. What happens when the crypto key zeroize rsa command is entered on a switch configured with the transport input ssh command on the vty lines?
A new RSA key pair is created.
The switch defaults to allowing Telnet connections only.
The switch is no longer able to make SSH connections as an SSH client.
The switch allows remote connections only after a new RSA key pair is generated.
52

Refer to the exhibit. All hosts are in listen mode. Host 1 and Host 4 both transmit data at the same time. How do the hosts respond on the network? (Choose two.)
After the end of the jam signal, a backoff algorithm is invoked.
Hosts 1 and 4 are operating full duplex so no collision will exist.
The hub will block the port connected to Host 4 to prevent a collision.
Hosts 1 and 4 are assigned shorter backoff values to provide them priority to access the media.
If a host has data to transmit after the backoff period of that host, the host checks to determine if the line is idle before transmitting.
![]()
![]()
![]()














































